WIDE IMAGE 3
 3) Memory: Frank Gehry.In their book about the architect, Frank Gehry (best known for his design of the Guggenheim museum in Bilbao, Spain), Jan Greenberg and Sandra Jordan (Frank O. Gehry: Outside In) describe the connection between Gehry’s childhood memories and his career in a way that resonates with the principle of the wide image.
3) Memory: Frank Gehry.In their book about the architect, Frank Gehry (best known for his design of the Guggenheim museum in Bilbao, Spain), Jan Greenberg and Sandra Jordan (Frank O. Gehry: Outside In) describe the connection between Gehry’s childhood memories and his career in a way that resonates with the principle of the wide image.
-
- Gehry’s grandmother was his best friend. He says she believed in strange, magical powers and superstitions. “When somebody would look at me funny, she would lick my face! I hated that, but I loved her a lot.”
Young Frank often spent the night at his grandparent’s house. They had emigrated to Canada from Poland, and although they slowly adopted the ways of their new country, they observed their Jewish traditions. On Thursdays, Frank went to the market with his grandmother. Each week she bought a live carp to be made into gefilte fish for Sabbath supper. They carried it home in a heavy white paper bag filled with water.
“We’d put it in the bathtub, and I would watch this fish for a day, this beautiful object swimming around. Then the next day it would be gone,” he says. Those beautiful disappearing fish, still vivid in his memories, appear over and over in Gehry’s architecture. . . .
In Timmins, Frank ran into his first experience with anti-Semitism. A group of bullies tormented him at school, beating him up and calling him Fish, an insult suggesting that he smelled. it was humiliating to be punched and taunted because he was Jewish. During this painful time he pulled back from his family’s religious beliefs. . . .
Many artists use autobiographical images to work through their conflicts. For Gehry, the shape of a fish repeated over and over in his designs represents his mixed feelings. On one hand, the fish echoes the anti-Semitic slurs of his childhood. On the other, it symbolizes the comforting religious rituals observed by his grandmother. The giant fish sculptures elevate memory into art.


 2) Childhood Memory: Einstein’s Themata.
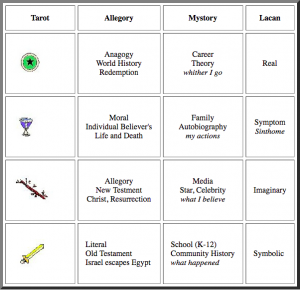
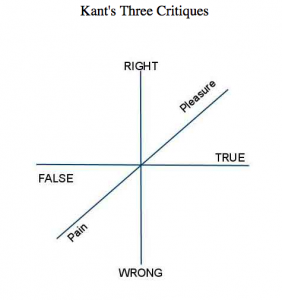
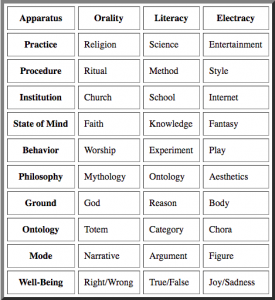
2) Childhood Memory: Einstein’s Themata.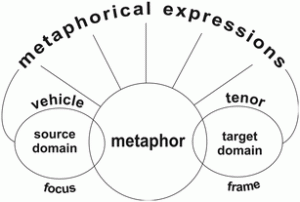 –Exercise. There is no need to understand all the features of mystory, wide image, heuretics, popcycle, before beginning the discovery and design project. We may begin with a memory exercise, to notice what scene remains in memory. The instructions are just to reflect for a few minutes on one’s early childhood, to observe what may appear, to take note, to save the scene for development later on. Record the memory in anecdote form (300-word flash fiction) illustrated with found images. The exercise may also be applied analytically to biographies of interest. We will inventory a number of cases of such early memories.
–Exercise. There is no need to understand all the features of mystory, wide image, heuretics, popcycle, before beginning the discovery and design project. We may begin with a memory exercise, to notice what scene remains in memory. The instructions are just to reflect for a few minutes on one’s early childhood, to observe what may appear, to take note, to save the scene for development later on. Record the memory in anecdote form (300-word flash fiction) illustrated with found images. The exercise may also be applied analytically to biographies of interest. We will inventory a number of cases of such early memories.