Cosmic Whiteness
The motif of metaphysical whiteness provides some practice with flash reason, conductive inference charting patterns emerging in the repeating signifiers of the popcycle. Such repetitions cause figurative and even archetypal connotation to emerge from ordinary scenes. To emphasize this design principle we include for the curricular archive a few touchstones of cosmic white in American letters.
For Once, Then, Something
Robert FrostOthers taunt me with having knelt at well-curbs
Always wrong to the light, so never seeing
Deeper down in the well than where the water
Gives me back in a shining surface picture
Me myself in the summer heaven godlike
Looking out of a wreath of fern and cloud puffs.
Once, when trying with chin against a well-curb,
I discerned, as I thought, beyond the picture,
Through the picture, a something white, uncertain,
Something more of the depths—and then I lost it.
Water came to rebuke the too clear water.
One drop fell from a fern, and lo, a ripple
Shook whatever it was lay there at bottom,
Blurred it, blotted it out. What was that whiteness?
Truth? A pebble of quartz? For once, then, something
–Melville, Moby Dick: the whiteness of the whale.
What the white whale was to Ahab, has been hinted; what, at times, he was to me, as yet remains unsaid. Aside from those more obvious considerations touching Moby Dick, which could not but occasionally awaken in any man’s soul some alarm, there was another thought, or rather vague, nameless horror concerning him, which at times by its intensity completely overpowered all the rest; and yet so mystical and well nigh ineffable was it, that I almost despair of putting it in a comprehensible form. It was the whiteness of the whale that above all things appalled me. But how can I hope to explain myself here; and yet, in some dim, random way, explain myself I must, else all these chapters might be naught. […]
But not yet have we solved the incantation of this whiteness, and learned why it appeals with such power to the soul; and more strange and far more portentous–why, as we have seen, it is at once the most meaning symbol of spiritual things, nay, the very veil of the Christian’s Deity; and yet should be as it is, the intensifying agent in things the most appalling to mankind.
Is it that by its indefiniteness it shadows forth the heartless voids and immensities of the universe, and thus stabs us from behind with the thought of annihilation, when beholding the white depths of the milky way? Or is it, that as in essence whiteness is not so much a colour as the visible absence of colour; and at the same time the concrete of all colours; is it for these reasons that there is such a dumb blankness, full of meaning, in a wide landscape of snows–a colourless, all-colour of atheism from which we shrink? And when we consider that other theory of the natural philosophers, that all other earthly hues–every stately or lovely emblazoning–the sweet tinges of sunset skies and woods; yea, and the gilded velvets of butterflies, and the butterfly cheeks of young girls; all these are but subtile deceits, not actually inherent in substances, but only laid on from without; so that all deified Nature absolutely paints like the harlot, whose allurements cover nothing but the charnel-house within; and when we proceed further, and consider that the mystical cosmetic which produces every one of her hues, the great principle of light, for ever remains white or colourless in itself, and if operating without medium upon matter, would touch all objects, even tulips and roses, with its own blank tinge–pondering all this, the palsied universe lies before us a leper; and like wilful travellers in Lapland, who refuse to wear coloured and colouring glasses upon their eyes, so the wretched infidel gazes himself blind at the monumental white shroud that wraps all the prospect around him. And of all these things the Albino whale was the symbol. Wonder ye then at the fiery hunt?
_____________
Image: Robert Rauschenberg, White Painting


 –After Nature. The work assigned in seminar, however, is After Nature. There are three worlds juxtaposed in this case, characterized as a triptych. The structure is thematized in the first section, about the sixteenth-century painter Matthias Grünewald, creator of perhaps the most famous triptych in art, the Isenheim Altarpiece. The second section is on the nineteenth-century botanist George Steller, and his journey into the Arctic with the expedition of Vitus Bering. The final section is an autobiographical prose poem. This section begins with testimony regarding the truth of a wide image, characterized as a memory fossil. “For it is hard to discover the winged vertebrates of prehistory embedded in tablets of slate. But if I see before me th nervature of past life in one image, I always think that this has something to with truth” (Sebald, 83). Then follows the scene of his existential epiphany (primal scene).
–After Nature. The work assigned in seminar, however, is After Nature. There are three worlds juxtaposed in this case, characterized as a triptych. The structure is thematized in the first section, about the sixteenth-century painter Matthias Grünewald, creator of perhaps the most famous triptych in art, the Isenheim Altarpiece. The second section is on the nineteenth-century botanist George Steller, and his journey into the Arctic with the expedition of Vitus Bering. The final section is an autobiographical prose poem. This section begins with testimony regarding the truth of a wide image, characterized as a memory fossil. “For it is hard to discover the winged vertebrates of prehistory embedded in tablets of slate. But if I see before me th nervature of past life in one image, I always think that this has something to with truth” (Sebald, 83). Then follows the scene of his existential epiphany (primal scene). I grew up, despite the dreadful course of events elsewhere, on the northern edge of the Alps, so it seems to me now, without any idea of destruction. But the habit of often falling down in the street and often sitting with bandaged hands by the open window between the potted fuchsias, waiting for the pain to subside and for hours doing nothing but looking out, early on induced me to imagine a silent catastrophe that occurs almost unperceived. What I thought at the time, while gazing down into the herb garden in which the nuns under their white starched hoods moved so slowly between the beds as though a moment ago they had still been caterpillars, this I have never got over. The emblem for me of the scarcely identifiable disaster since that time has been a stunted Tatar with a red headcloth and a white slightly curved feather. In anthropology this figure is often associated with certain forms of self-mutilation and described as that of the adept who ascends a snow-covered mountain and long tarries there, as they say, in tears. (Sebald, After Nature, 89-90).
I grew up, despite the dreadful course of events elsewhere, on the northern edge of the Alps, so it seems to me now, without any idea of destruction. But the habit of often falling down in the street and often sitting with bandaged hands by the open window between the potted fuchsias, waiting for the pain to subside and for hours doing nothing but looking out, early on induced me to imagine a silent catastrophe that occurs almost unperceived. What I thought at the time, while gazing down into the herb garden in which the nuns under their white starched hoods moved so slowly between the beds as though a moment ago they had still been caterpillars, this I have never got over. The emblem for me of the scarcely identifiable disaster since that time has been a stunted Tatar with a red headcloth and a white slightly curved feather. In anthropology this figure is often associated with certain forms of self-mutilation and described as that of the adept who ascends a snow-covered mountain and long tarries there, as they say, in tears. (Sebald, After Nature, 89-90). Our first memories are visual ones. In memory life becomes a silent film. We all have in our minds an image which is the first, or one of the first, in our lives. That image is a sign, or to be exact, a linguistic sign. So if it is a linguistic sign it communicates or expresses something. I shall give you an example. The first image of my life is a white, transparent bind, which hangs–without moving, I believe–from a window which looks out on to a somewhat sad and dark lane. That blind terrifies me and fills me with anguish: not as something threatening and unpleasant but as something cosmic. In that blind the spirit of the middle-class house in Bologna where I was born is summed up and takes bodily form. Indeed the images which compete with the blind for chronological primacy are a room with an alcove (where my grandmother slept), heavy “proper” furniture, a carriage in the street which I wanted to climb into. These images are less painful than that of the blind, yet in them too there is concentrated that element of the cosmic which constitutes the petty bourgeois spirit of the world into which I was born. But if in the objects and things the images which have remained firmly in my memory (like those of an indelible dream) there is precipitated and concentrated the whole world of “memories,” which is recalled by those images in a single instant– if, that is to say, those object and those things are containers in which is stored a universe which I can extract and look at, then, at the same time, these objects and things are also something other than a container. . . . So their communication was essentially instructional. They taught me where I had been born, in what world I lived, and above all how to think about my birth and my life. Since it was a question of an unarticulated, fixed and incontrovertible pedagogic discourse, it could not be other–as we say today–than authoritarian and repressive. What that blind said to me and taught me did not admit (and does not admit) of rejoinders. No dialogue was possible or admissible with it, nor any act of self-education. That is why I believed that the whole world was the world which that blind taught me: that is to say, I thought that the whole world was “proper,” idealistic, sad and skeptical, a little vulgar–in short, petty bourgeois. (Pier Paolo Pasolini, Lutheran Letters, trans. Stuart Hood. Carcanet Press: New York, 1987).
Our first memories are visual ones. In memory life becomes a silent film. We all have in our minds an image which is the first, or one of the first, in our lives. That image is a sign, or to be exact, a linguistic sign. So if it is a linguistic sign it communicates or expresses something. I shall give you an example. The first image of my life is a white, transparent bind, which hangs–without moving, I believe–from a window which looks out on to a somewhat sad and dark lane. That blind terrifies me and fills me with anguish: not as something threatening and unpleasant but as something cosmic. In that blind the spirit of the middle-class house in Bologna where I was born is summed up and takes bodily form. Indeed the images which compete with the blind for chronological primacy are a room with an alcove (where my grandmother slept), heavy “proper” furniture, a carriage in the street which I wanted to climb into. These images are less painful than that of the blind, yet in them too there is concentrated that element of the cosmic which constitutes the petty bourgeois spirit of the world into which I was born. But if in the objects and things the images which have remained firmly in my memory (like those of an indelible dream) there is precipitated and concentrated the whole world of “memories,” which is recalled by those images in a single instant– if, that is to say, those object and those things are containers in which is stored a universe which I can extract and look at, then, at the same time, these objects and things are also something other than a container. . . . So their communication was essentially instructional. They taught me where I had been born, in what world I lived, and above all how to think about my birth and my life. Since it was a question of an unarticulated, fixed and incontrovertible pedagogic discourse, it could not be other–as we say today–than authoritarian and repressive. What that blind said to me and taught me did not admit (and does not admit) of rejoinders. No dialogue was possible or admissible with it, nor any act of self-education. That is why I believed that the whole world was the world which that blind taught me: that is to say, I thought that the whole world was “proper,” idealistic, sad and skeptical, a little vulgar–in short, petty bourgeois. (Pier Paolo Pasolini, Lutheran Letters, trans. Stuart Hood. Carcanet Press: New York, 1987).
 When it comes to the image of wide scope (four or five fundamental images structuring imagination, and central to the history of invention), the prototype is Einstein’s compass (received from his father as a gift at age four or five): the wide image is a compass for the existential positioning system of learning, to orient egents tracking the vector of invention.
When it comes to the image of wide scope (four or five fundamental images structuring imagination, and central to the history of invention), the prototype is Einstein’s compass (received from his father as a gift at age four or five): the wide image is a compass for the existential positioning system of learning, to orient egents tracking the vector of invention. Popcycle. Learning is a complex adaptive system, and an aspect of what we are exploring is a certain isomorphism transversing all such systems. Heuretic pedagogy is describable within a systems perspective, beginning with the
Popcycle. Learning is a complex adaptive system, and an aspect of what we are exploring is a certain isomorphism transversing all such systems. Heuretic pedagogy is describable within a systems perspective, beginning with the 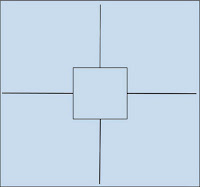 –Mandala. A basic diagram (popcycle mandala) is used consistently throughout KE to map and correlate correspondences across the layers and levels of the popcycle-mystory-wide image as Interface for the Stack of digital civilization. The diagram is not original, but is appropriated from various fourfold system templates. The diagram below registers the CATTt of a seminar documented in Ulmer’s blog,
–Mandala. A basic diagram (popcycle mandala) is used consistently throughout KE to map and correlate correspondences across the layers and levels of the popcycle-mystory-wide image as Interface for the Stack of digital civilization. The diagram is not original, but is appropriated from various fourfold system templates. The diagram below registers the CATTt of a seminar documented in Ulmer’s blog, 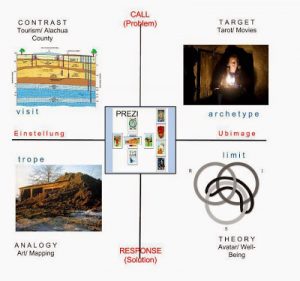
 From Agent to Egent. These posts undertake a meandering trace of inquiry. KE reviews Ulmer’s work of the past four+ decades in order to understand it again, whole, as if given all at once, in a flash of insight. Egents undertaking konsult are interlocutors, collaborators, tutors. The purpose is to compose and design a discourse on method, in the tradition running from Plato’s Phaedrus to contemporary French philosophy, describing and testing a mode of learning native to electracy (the digital apparatus). The outline necessarily begins in literacy and school. The coming pedagogy is also explored elsewhere, in the context of EmerAgency (conceptual konsulting, without portfolio), addressing the curriculum reform in progress at MIT as well as Digital Humanities institutionalization. The discussion across disciplines concerns TPE (Theopraxesis)–a shared interest in learning how to learn in digital civilization, using heuretics, the logic of invention.
From Agent to Egent. These posts undertake a meandering trace of inquiry. KE reviews Ulmer’s work of the past four+ decades in order to understand it again, whole, as if given all at once, in a flash of insight. Egents undertaking konsult are interlocutors, collaborators, tutors. The purpose is to compose and design a discourse on method, in the tradition running from Plato’s Phaedrus to contemporary French philosophy, describing and testing a mode of learning native to electracy (the digital apparatus). The outline necessarily begins in literacy and school. The coming pedagogy is also explored elsewhere, in the context of EmerAgency (conceptual konsulting, without portfolio), addressing the curriculum reform in progress at MIT as well as Digital Humanities institutionalization. The discussion across disciplines concerns TPE (Theopraxesis)–a shared interest in learning how to learn in digital civilization, using heuretics, the logic of invention. “Gest” is not supposed to mean gesticulation: it is not a matter of explana-tory or emphatic movements of the hands, but of overall attitudes. A language is gestic when it is grounded in a gest and conveys particular attitudes adopted by the speaker towards other men. The sentence “pluck the eye that offends thee out” is less effective from the gestic point of view than “if thine eve offend thee, pluck it out.” The latter starts by pre-senting the eye, and the first clause has the definite gest of making an assumption; the main clause then comes as a surprise, a piece of advice, and a relief.
“Gest” is not supposed to mean gesticulation: it is not a matter of explana-tory or emphatic movements of the hands, but of overall attitudes. A language is gestic when it is grounded in a gest and conveys particular attitudes adopted by the speaker towards other men. The sentence “pluck the eye that offends thee out” is less effective from the gestic point of view than “if thine eve offend thee, pluck it out.” The latter starts by pre-senting the eye, and the first clause has the definite gest of making an assumption; the main clause then comes as a surprise, a piece of advice, and a relief. Suppose that the musician composing a cantata on Lenin’s death has to reproduce his own attitude to the class struggle. As far as the gest goes, there are a number of different ways in which the report of Lenin’s death can be set. A certain dignity of presentation means little, since where death is involved this could also be held to be fitting in the case of an enemy. Anger at ‘the blind workings of providence’ cutting short the lives of the best members of the community would not be a communist gest; nor would a wise resignation to “life’s irony”; for the gest of communists mourning a communist is a very special one. The musician’s attitude to his text, the spokesman’s to his report, shows the extent of his political, and so of his human maturity. A man’s stature is shown by what he mourns and in what way he mourns it. To raise mourning to a high plane, to make it into an element of social progress: that is an artistic task.
Suppose that the musician composing a cantata on Lenin’s death has to reproduce his own attitude to the class struggle. As far as the gest goes, there are a number of different ways in which the report of Lenin’s death can be set. A certain dignity of presentation means little, since where death is involved this could also be held to be fitting in the case of an enemy. Anger at ‘the blind workings of providence’ cutting short the lives of the best members of the community would not be a communist gest; nor would a wise resignation to “life’s irony”; for the gest of communists mourning a communist is a very special one. The musician’s attitude to his text, the spokesman’s to his report, shows the extent of his political, and so of his human maturity. A man’s stature is shown by what he mourns and in what way he mourns it. To raise mourning to a high plane, to make it into an element of social progress: that is an artistic task. Here is Existential Positioning (EPS) in experience. How common is it to have an intuition of mortality during childhood? It is as if each person has to realize for him/herself individually what the sages codified in Ancient philosophy as ataraxy. Ataraxy is a state of mind in which the sage, realizing that s/he has no control over external events, decides to reduce her/his own desires. This ascetic view is associated with the stance that “philosophy is learning how to die.” Paradoxically, it may seem, philosophers insist that the realization that everyone dies is liberating. Since death is inevitable, why get so excited over one’s successes and failures in life? Of course, various response to this intuition are possible, such as carpe diem (seize the day).
Here is Existential Positioning (EPS) in experience. How common is it to have an intuition of mortality during childhood? It is as if each person has to realize for him/herself individually what the sages codified in Ancient philosophy as ataraxy. Ataraxy is a state of mind in which the sage, realizing that s/he has no control over external events, decides to reduce her/his own desires. This ascetic view is associated with the stance that “philosophy is learning how to die.” Paradoxically, it may seem, philosophers insist that the realization that everyone dies is liberating. Since death is inevitable, why get so excited over one’s successes and failures in life? Of course, various response to this intuition are possible, such as carpe diem (seize the day). A primal scene? The boy is eleven, starting seventh grade. His father explains that it is time to learn the value of work. He has arranged a job for his son with a friend whose name is Cutting and who owns a sheet metal shop. Every Saturday the boy rides his bicycle across town to Cutting’s Sheet Metal. The employees are done for the week at noon on Saturday. He has to arrive by noon so the boss can lock up, leaving the boy inside (he is too young to be trusted with a key). The job is to clean the shop — sweep the floor, gather up the tools and align them neatly in their designated places on the work benches, collect the remnants and clippings of the metal sheets scattered everywhere. It takes most of the afternoon to finish the chores. The shop is a cavernous open warehouse, with rows of heavy tables, the walls lined with shelves stacked to the distant ceiling with equipment, tools, metals. It is quiet, the stillness of dust motes swirling in the beams of sunlight filtered through the few windows high up near the roof, carving vectors through deep shadow. The sunlight catches the edges of a museum of blades, a taxonomy of every snipping snap slice chop saw hack rend rip cleave nip or severing machine. Half-shaped tin objects stand in rows behind piles of hammers and modelling frames. After so many weeks and months of Saturday noons the boy begins to lose touch with his former friends and companions, who go their separate ways.
A primal scene? The boy is eleven, starting seventh grade. His father explains that it is time to learn the value of work. He has arranged a job for his son with a friend whose name is Cutting and who owns a sheet metal shop. Every Saturday the boy rides his bicycle across town to Cutting’s Sheet Metal. The employees are done for the week at noon on Saturday. He has to arrive by noon so the boss can lock up, leaving the boy inside (he is too young to be trusted with a key). The job is to clean the shop — sweep the floor, gather up the tools and align them neatly in their designated places on the work benches, collect the remnants and clippings of the metal sheets scattered everywhere. It takes most of the afternoon to finish the chores. The shop is a cavernous open warehouse, with rows of heavy tables, the walls lined with shelves stacked to the distant ceiling with equipment, tools, metals. It is quiet, the stillness of dust motes swirling in the beams of sunlight filtered through the few windows high up near the roof, carving vectors through deep shadow. The sunlight catches the edges of a museum of blades, a taxonomy of every snipping snap slice chop saw hack rend rip cleave nip or severing machine. Half-shaped tin objects stand in rows behind piles of hammers and modelling frames. After so many weeks and months of Saturday noons the boy begins to lose touch with his former friends and companions, who go their separate ways. What happens then? The light and shadow of the industrial building open all at once onto a void, a black hole and white wall of divided worlds in this little infinite town: the official world of adults (parents, teachers, coaches, ministers, scout masters) that until then had constituted reality, and the unofficial world of his peers, whose existence he had only just discovered. Two completely different systems of virtue and vice, success and failure, winning and losing, visibility and invisibility, were enforced in these realms: systems Not only different, but opposite and in conflict. What earned admiration and respect in one was inversely judged in the other. He could not have articulated the revelation so abstractly then. The unexpected aspect of this scene is the sense of abandonment, solitary isolation, that overcomes the child, a spilling out or abjection, an absolute exhaling of substance, followed soon after by the inhaled relief of knowing that it doesn’t matter, since everyone and everything dies everywhere the same death.
What happens then? The light and shadow of the industrial building open all at once onto a void, a black hole and white wall of divided worlds in this little infinite town: the official world of adults (parents, teachers, coaches, ministers, scout masters) that until then had constituted reality, and the unofficial world of his peers, whose existence he had only just discovered. Two completely different systems of virtue and vice, success and failure, winning and losing, visibility and invisibility, were enforced in these realms: systems Not only different, but opposite and in conflict. What earned admiration and respect in one was inversely judged in the other. He could not have articulated the revelation so abstractly then. The unexpected aspect of this scene is the sense of abandonment, solitary isolation, that overcomes the child, a spilling out or abjection, an absolute exhaling of substance, followed soon after by the inhaled relief of knowing that it doesn’t matter, since everyone and everything dies everywhere the same death. The method is counterintuitive, in that egents turn away from the historical catastrophe, in order to access their peculiar power. The instructions derived from the text are to compose a figure by juxtaposing a childhood memory with a collective event (a disaster). Blanchot calls this memory a primal scene. It represents an early if not first experience of self-awareness of the human condition – an existential intuition. The corresponding event for Blanchot is the Holocaust.
The method is counterintuitive, in that egents turn away from the historical catastrophe, in order to access their peculiar power. The instructions derived from the text are to compose a figure by juxtaposing a childhood memory with a collective event (a disaster). Blanchot calls this memory a primal scene. It represents an early if not first experience of self-awareness of the human condition – an existential intuition. The corresponding event for Blanchot is the Holocaust. (A primal scene?) You who live later, close to a heart that beats no more, suppose, suppose this: the child – is he seven years old, or eight perhaps? – standing by the window, drawing the curtain and, through the pane, looking. What he sees: the garden, the wintry trees, the wall of a house. Though he sees, no doubt in a child’s way, his play space, he grows weary and slowly looks up toward the ordinary sky, with clouds, grey light – pallid daylight without depth.
(A primal scene?) You who live later, close to a heart that beats no more, suppose, suppose this: the child – is he seven years old, or eight perhaps? – standing by the window, drawing the curtain and, through the pane, looking. What he sees: the garden, the wintry trees, the wall of a house. Though he sees, no doubt in a child’s way, his play space, he grows weary and slowly looks up toward the ordinary sky, with clouds, grey light – pallid daylight without depth.