Wide Image: Diagram
 Wide Image into Diagram. The next step after using the emblem catechism to generate wide image is to begin translation into diagrams, extracting patterns from the intervals and relationships emerging within the matrix. Composing my first mystory in the mid-1980s, “Derrida at the Little Bighorn,” I discovered a match between Family and Career that produced an epiphany I have developed ever since. One of my first jobs when I worked at the plant was to clean the grids of the screens used to grade the gravel into sizes. Eventually the screens plugged up with stones and I had to knock them loose with a hammer. The pea-gravel screen could be cleaned by running the tip of a large screwdriver along the meshed grids, which produced an almost musical sound. This was the actual “gravel plant.” The washer with its three grades of screen, one on top of the other, was fed by a conveyor belt carrying the pit gravel from the quarry, and fed in turn three piles of sized rock, with the sand coming out the bottom. The whole contraption made a terrible noise and shook violently. I realized years later, reading Plato’s Timaeus after Derrida, that this gravel washer was a good metaphor or model for the operation of chora, sorting chaos into Earth, Air, Fire, Water.
Wide Image into Diagram. The next step after using the emblem catechism to generate wide image is to begin translation into diagrams, extracting patterns from the intervals and relationships emerging within the matrix. Composing my first mystory in the mid-1980s, “Derrida at the Little Bighorn,” I discovered a match between Family and Career that produced an epiphany I have developed ever since. One of my first jobs when I worked at the plant was to clean the grids of the screens used to grade the gravel into sizes. Eventually the screens plugged up with stones and I had to knock them loose with a hammer. The pea-gravel screen could be cleaned by running the tip of a large screwdriver along the meshed grids, which produced an almost musical sound. This was the actual “gravel plant.” The washer with its three grades of screen, one on top of the other, was fed by a conveyor belt carrying the pit gravel from the quarry, and fed in turn three piles of sized rock, with the sand coming out the bottom. The whole contraption made a terrible noise and shook violently. I realized years later, reading Plato’s Timaeus after Derrida, that this gravel washer was a good metaphor or model for the operation of chora, sorting chaos into Earth, Air, Fire, Water.
–Plato, Timaeus, 52D-53A (Chora).
“My verdict is that being and space and generation, these three, existed in their three ways before the heaven, and that the nurse of generation, moistened by water and inflamed by fire, and receiving the forms of earth and air, and experiencing all the affections which accompany these, presented a strange variety of appearances. and being full of powers which were neither similar nor equally balanced, was never in any part in a state of equipoise, but swaying unevenly hither and thither, was shaken by them, and by its motion again shook them, and the elements when moved were separated and carried continually, some one way, some another. As, when grain is shaken and winnowed by fans and other instruments used in the threshing of corn, the close and heavy particles are borne away and settle in one direction, and the loose and light particles in another. In this manner, the four kinds of elements were then shaken by the receiving vessel, which, moving like a winnowing machine, scattered far away from one another the elements most unlike, and forced the most similar elements into close contact.”
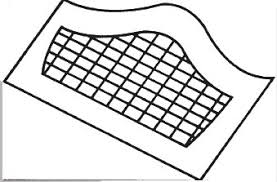 –Derrida, Chora-L As part of his collaboration with the architect, Peter Eisenman, on a design for one of the folies, to be included in the Park for Creativity, Parc de la Villette, in Paris, Derrida produced a drawing and a descriptive concept for an impossible project: to build Chora. “I propose therefore the following ‘materialisation’: in one or three exemplars (with different scalings) a gilded metallic object will be planted obliquely in the ground. Neither vertical nor horizontal, a most solid frame will resemble at once a mesh, sieve, or grid and a stringed musical instrument. An interpretive and selective filter which will have permitted a reading and sifting of the three sites [at the Park] and the three embeddings.”
–Derrida, Chora-L As part of his collaboration with the architect, Peter Eisenman, on a design for one of the folies, to be included in the Park for Creativity, Parc de la Villette, in Paris, Derrida produced a drawing and a descriptive concept for an impossible project: to build Chora. “I propose therefore the following ‘materialisation’: in one or three exemplars (with different scalings) a gilded metallic object will be planted obliquely in the ground. Neither vertical nor horizontal, a most solid frame will resemble at once a mesh, sieve, or grid and a stringed musical instrument. An interpretive and selective filter which will have permitted a reading and sifting of the three sites [at the Park] and the three embeddings.”
–

 –Tenor (Themata): Catechism. The image on the left is the emblem Ulmer generated from his mystory, leading to design of his wide image in
–Tenor (Themata): Catechism. The image on the left is the emblem Ulmer generated from his mystory, leading to design of his wide image in  3) The third question is Mood: given the necessity to act in that way, in a world of that character, how do I feel? Wabi-Sabi advises acceptance of the inevitable and appreciation of the cosmic order. Ulmer found his state of mind expressed in High Noon as a fable of duty: despite his contempt for the hypocritical community, the sheriff fought the gang of killers, after which he threw away the tin star. This gesture of discarding the badge of status determined the tin star as the icon of the emblem. In practice it is best to decide which popcycle story supplies the picture, and which question of the catechism that story answers, and the rest of the emblem follows from there.
3) The third question is Mood: given the necessity to act in that way, in a world of that character, how do I feel? Wabi-Sabi advises acceptance of the inevitable and appreciation of the cosmic order. Ulmer found his state of mind expressed in High Noon as a fable of duty: despite his contempt for the hypocritical community, the sheriff fought the gang of killers, after which he threw away the tin star. This gesture of discarding the badge of status determined the tin star as the icon of the emblem. In practice it is best to decide which popcycle story supplies the picture, and which question of the catechism that story answers, and the rest of the emblem follows from there. –How an Image becomes Wide. Koren demonstrates how a detail of the world is selected as a vehicle for a poetic image: for example, a worn shingle on an old hut, with a streak of rust descending from an iron nail. The tenor (theme) of this vehicle is coded in Japanese traditional culture, relative to the wisdom metaphysics of Buddhism, to express an existential insight into time and entropy known as wabi-sabi. “Wabi-Sabi can be called a ‘comprehensive’ aesthetic system. Its world view, or universe, is self-referential. It provides an integrated approach to the ultimate nature of existence (metaphysics), sacred knowledge (spirituality), emotional well-being (state of mind), behavior (morality), and the look and feel of things (materiality)” (Koren, 41). The instruction was not to seek Wabi-Sabi in one’s own experience, but the equivalent, the mood and atmosphere, to find one’s personal version of what was modeled in Japanese tradition. The folk traditions of Blues into Jazz in global Creole syncretism (mufarse into tango, saudade into samba) is central to the thymotic and erotic dimension of world materialized in digital electracy. Koren’s analysis demonstrates how to expand the two-part vehicle and tenor of image into a six-part inventory. Students generated their emblems productive of wide image by answer six questions posed by Koren: three for vehicle; three for tenor. The three questions addressing tenor (themata) are the same three articulated in the catechism of modernism, directing theopraxesis. One implication, to be developed further, is that the system of capabilities is not confined to the Western Tradition, but functions globally across cultures and civilizations.
–How an Image becomes Wide. Koren demonstrates how a detail of the world is selected as a vehicle for a poetic image: for example, a worn shingle on an old hut, with a streak of rust descending from an iron nail. The tenor (theme) of this vehicle is coded in Japanese traditional culture, relative to the wisdom metaphysics of Buddhism, to express an existential insight into time and entropy known as wabi-sabi. “Wabi-Sabi can be called a ‘comprehensive’ aesthetic system. Its world view, or universe, is self-referential. It provides an integrated approach to the ultimate nature of existence (metaphysics), sacred knowledge (spirituality), emotional well-being (state of mind), behavior (morality), and the look and feel of things (materiality)” (Koren, 41). The instruction was not to seek Wabi-Sabi in one’s own experience, but the equivalent, the mood and atmosphere, to find one’s personal version of what was modeled in Japanese tradition. The folk traditions of Blues into Jazz in global Creole syncretism (mufarse into tango, saudade into samba) is central to the thymotic and erotic dimension of world materialized in digital electracy. Koren’s analysis demonstrates how to expand the two-part vehicle and tenor of image into a six-part inventory. Students generated their emblems productive of wide image by answer six questions posed by Koren: three for vehicle; three for tenor. The three questions addressing tenor (themata) are the same three articulated in the catechism of modernism, directing theopraxesis. One implication, to be developed further, is that the system of capabilities is not confined to the Western Tradition, but functions globally across cultures and civilizations. –Poetics: Image expanded into Emblem. The expanded image consists of two registers: material; metaphysical. Working with the narratives generated in composition of mystory, students must commit to one pedagogical object (magic tool), some detail found in at least one of the diegesis of the popcycle, to serve as logo or brand icon for the wide image. In Ulmer’s case (Noon Star), the repeating detail (like the dogs repeating in Momaday’s section III) was a five-pointed star: Family memory (the red star on his sheet music of the march, Garry Owen; Entertainment mythology (the film High Noon, Gary Cooper as Will Kane, discarding his sheriff’s star in the dirt after the gun fight); Community history (“General” Custer’s badge of rank, and Indian name, Son of the Morning Star). The three material questions are: 1) what is the prop/ icon? Ulmer chose the tin star sheriff’s badge to represent this materiality. 2) What are its attributes? (what mood or atmosphere is expressed that distinguishes this icon from its archetype, configuring it specifically for me. The context of High Noon star thrown in the dirt expresses rejection and disgust with the hypocritical authority symbolized in the badge. 3) Archetype: what is the conventional meaning associated with this icon in the archive? (the five-pointed star has an extensive presence throughout many cultures).
–Poetics: Image expanded into Emblem. The expanded image consists of two registers: material; metaphysical. Working with the narratives generated in composition of mystory, students must commit to one pedagogical object (magic tool), some detail found in at least one of the diegesis of the popcycle, to serve as logo or brand icon for the wide image. In Ulmer’s case (Noon Star), the repeating detail (like the dogs repeating in Momaday’s section III) was a five-pointed star: Family memory (the red star on his sheet music of the march, Garry Owen; Entertainment mythology (the film High Noon, Gary Cooper as Will Kane, discarding his sheriff’s star in the dirt after the gun fight); Community history (“General” Custer’s badge of rank, and Indian name, Son of the Morning Star). The three material questions are: 1) what is the prop/ icon? Ulmer chose the tin star sheriff’s badge to represent this materiality. 2) What are its attributes? (what mood or atmosphere is expressed that distinguishes this icon from its archetype, configuring it specifically for me. The context of High Noon star thrown in the dirt expresses rejection and disgust with the hypocritical authority symbolized in the badge. 3) Archetype: what is the conventional meaning associated with this icon in the archive? (the five-pointed star has an extensive presence throughout many cultures). Haiku Reason. Spring Break of 1980 I went to Europe and met Joseph Beuys in Düsseldorf and Jacques Derrida in Paris, protagonists of Applied Grammatology (1985). The other adopted mentor I wanted to meet, Roland Barthes (inspiration for Teletheory, 1989), was fatally injured in an accident just a few days before I arrived in Paris. On the strength of reading Barthes’s Camera Lucida, published late in his career, in which he theorized image logic by analogy with Japanese haiku poetry, I based my introduction to image thinking in Internet Invention on haiku reason (synonymous with reasoneon). What I didn’t know was that at the time of his accident Barthes had just completed a seminar in which the fall semester was devoted entirely to haiku poetry as a foundation for thinking about imaging in general: The Preparation of the Novel, English, translation published 2011. We will return to late Barthes, whose A Lover’s Discourse: Fragments, is a relay for mystory (in Teletheory). Japonisme in any case played a major role in the invention of modernism in France, a symptom of the syncretism underway throughout the colonial period forming a hybrid of Western and Eastern civilizations, with artists creating the cyberpidgin language made necessary by the trade routes opened by the corporation, the new institution of electracy (East India Company, 1600). In this context, Barthes’s example motivated a closer look at Japonisme in particular and Eastern resources in general.
Haiku Reason. Spring Break of 1980 I went to Europe and met Joseph Beuys in Düsseldorf and Jacques Derrida in Paris, protagonists of Applied Grammatology (1985). The other adopted mentor I wanted to meet, Roland Barthes (inspiration for Teletheory, 1989), was fatally injured in an accident just a few days before I arrived in Paris. On the strength of reading Barthes’s Camera Lucida, published late in his career, in which he theorized image logic by analogy with Japanese haiku poetry, I based my introduction to image thinking in Internet Invention on haiku reason (synonymous with reasoneon). What I didn’t know was that at the time of his accident Barthes had just completed a seminar in which the fall semester was devoted entirely to haiku poetry as a foundation for thinking about imaging in general: The Preparation of the Novel, English, translation published 2011. We will return to late Barthes, whose A Lover’s Discourse: Fragments, is a relay for mystory (in Teletheory). Japonisme in any case played a major role in the invention of modernism in France, a symptom of the syncretism underway throughout the colonial period forming a hybrid of Western and Eastern civilizations, with artists creating the cyberpidgin language made necessary by the trade routes opened by the corporation, the new institution of electracy (East India Company, 1600). In this context, Barthes’s example motivated a closer look at Japonisme in particular and Eastern resources in general. Pachinko
Pachinko –Fable: What resources are available for inquiry and expression in the conditions after Nietzsche, the history of an error, after the simultaneous withdrawal of the true world and the apparent world along with it? The time is noon (the shortest shadow). What remains is fable, Nietzsche said. What are the possibilities of fable as genre? Duchamp improvised one approach, perhaps not even yet fully appreciated. His Readymades are fables, albeit weak (faible) fables, in that they provide the illustrations only (the emblems, impresas). He intimated his variation on the mode with his most notorious instance, whose title “Fountain” translates “La Fontaine,” antonomasia between common and proper noun, evoking the name of the author of many fables in the common “fountain,” itself a euphemistic title for a urinal. Ulmer’s collage of the urinal with a cover of La Fontaine’s book make the joke explicit. Duchamp’s commitment to the punning bachelor machine logic central to modernism is well known. He acknowledged his attendance at a performance of a stage adaptation of Raymond Roussel’s 1910 novel Impressions of Africa as a turning point in his career (Roussel’s method of composition used generative puns). It has been suggested that some of the Readymades at least are comments on dreams described in Freud’s Interpretation of Dreams, hence that they use rebus methods (visualizations evoking words). Freud noted, for example, that many dreams are triggered when sleepers experience the need to urinate (the dream allows sleep to continue briefly). The text of the fabled fountain is provided by its history, being as it is the most influential (if not the “best”) art work of the twentieth century, including its status as a prank, and all the manipulations Duchamp performed to put the image of La Fontaine into circulation, recorded in Thierry De Duve’s Kant After Duchamp. What is the moral of the readymade fable?
–Fable: What resources are available for inquiry and expression in the conditions after Nietzsche, the history of an error, after the simultaneous withdrawal of the true world and the apparent world along with it? The time is noon (the shortest shadow). What remains is fable, Nietzsche said. What are the possibilities of fable as genre? Duchamp improvised one approach, perhaps not even yet fully appreciated. His Readymades are fables, albeit weak (faible) fables, in that they provide the illustrations only (the emblems, impresas). He intimated his variation on the mode with his most notorious instance, whose title “Fountain” translates “La Fontaine,” antonomasia between common and proper noun, evoking the name of the author of many fables in the common “fountain,” itself a euphemistic title for a urinal. Ulmer’s collage of the urinal with a cover of La Fontaine’s book make the joke explicit. Duchamp’s commitment to the punning bachelor machine logic central to modernism is well known. He acknowledged his attendance at a performance of a stage adaptation of Raymond Roussel’s 1910 novel Impressions of Africa as a turning point in his career (Roussel’s method of composition used generative puns). It has been suggested that some of the Readymades at least are comments on dreams described in Freud’s Interpretation of Dreams, hence that they use rebus methods (visualizations evoking words). Freud noted, for example, that many dreams are triggered when sleepers experience the need to urinate (the dream allows sleep to continue briefly). The text of the fabled fountain is provided by its history, being as it is the most influential (if not the “best”) art work of the twentieth century, including its status as a prank, and all the manipulations Duchamp performed to put the image of La Fontaine into circulation, recorded in Thierry De Duve’s Kant After Duchamp. What is the moral of the readymade fable? –Martin Kippenberger, “Rameau’s Nephew,” 1988
–Martin Kippenberger, “Rameau’s Nephew,” 1988 This pictorial tradition can be traced back to an engraving by Marc Antonio. It shows an almost naked woman of Giorgionesque type watering a flower. This enigmatic motif can be explained with the help of the literary tradition. It is a symbol of “Grammatica.” As the plant grows through watering so the young mind is formed through the study of grammar. In late antiquity grammar became the foundation of the liberal arts.
This pictorial tradition can be traced back to an engraving by Marc Antonio. It shows an almost naked woman of Giorgionesque type watering a flower. This enigmatic motif can be explained with the help of the literary tradition. It is a symbol of “Grammatica.” As the plant grows through watering so the young mind is formed through the study of grammar. In late antiquity grammar became the foundation of the liberal arts.

 Catechism: Wide Image. The catechism of modernism (drawing on the Western Tradition) is articulated in Kant’s philosophy and Gauguin’s painting. The answers to the questions are specific to each person, and are generated during the composition of the wide image. Several posts are required to unfold this poetics, by means of which egents learn to actualize in their own projects the intelligence potential (latent) in the cultural archive. This archive in its global version functions for electracy the way Avatar functioned for orality: source of absolute knowledge (the project of Avatar Emergency was learning to receive this communication of Avatar). One of the first things that happens in transition from one apparatus to another is the mise en machine of the previous apparatus. As McLuhan observed, the content of the new medium is the old medium (literacy put oral mythologies into writing; electracy digitized the libraries). The remainder of the apparatus epoch is devoted to invention and diffusion throughout society of the new metaphysics (operating practices).
Catechism: Wide Image. The catechism of modernism (drawing on the Western Tradition) is articulated in Kant’s philosophy and Gauguin’s painting. The answers to the questions are specific to each person, and are generated during the composition of the wide image. Several posts are required to unfold this poetics, by means of which egents learn to actualize in their own projects the intelligence potential (latent) in the cultural archive. This archive in its global version functions for electracy the way Avatar functioned for orality: source of absolute knowledge (the project of Avatar Emergency was learning to receive this communication of Avatar). One of the first things that happens in transition from one apparatus to another is the mise en machine of the previous apparatus. As McLuhan observed, the content of the new medium is the old medium (literacy put oral mythologies into writing; electracy digitized the libraries). The remainder of the apparatus epoch is devoted to invention and diffusion throughout society of the new metaphysics (operating practices). –Emblem. The translation of mystory into wide image is mediated by emblematics. The emblem (having the same structure as a generic advertisement), considering its historical relationship with allegory, expresses in condensed form the image of wide scope ( sinthome, Lacan) that emerges in the making of a mystory (it embodies the pattern of signifiers that repeat when the makers situation is mapped across the popcycle). Studio and Textshop exercises explore the form, including its history from its introduction in the Renaissance through to contemporary advertising. An advantage of the form is just this combination of archival presence and pop familiarity. Ulmer designed this emblem based on his mystory: Motto is “pithy,” aphoristic, allusive, to produce an evocative connotation when combined with the picture. The epigraph is informational, clarifying what is suggested in the motto-picture juxtaposition.
–Emblem. The translation of mystory into wide image is mediated by emblematics. The emblem (having the same structure as a generic advertisement), considering its historical relationship with allegory, expresses in condensed form the image of wide scope ( sinthome, Lacan) that emerges in the making of a mystory (it embodies the pattern of signifiers that repeat when the makers situation is mapped across the popcycle). Studio and Textshop exercises explore the form, including its history from its introduction in the Renaissance through to contemporary advertising. An advantage of the form is just this combination of archival presence and pop familiarity. Ulmer designed this emblem based on his mystory: Motto is “pithy,” aphoristic, allusive, to produce an evocative connotation when combined with the picture. The epigraph is informational, clarifying what is suggested in the motto-picture juxtaposition. –Advertisement.The Marlboro Cowboy
–Advertisement.The Marlboro Cowboy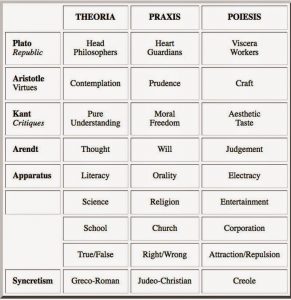
 Capability. As these posts accumulate across an expanding set of categories, it is important to recall the focus of KE. Konsult learns the writing of the disaster in three dimensions: heuretics (invention), wide image (mystory), theopraxesis (capability). So far we have assumed some disaster addresses us, and devoted our attention to the heuretics of mystory, learning how to design an image of wide scope, source of our original hypothesis responding to disaster. Konsult takes up for electracy an ancient, even primordial drama: the striving to persist in one’s own being (to live), that Spinoza called Conatus, against the Overwhelming force of resistance, entropy, death. Heidegger characterized the drama as Riss, exploiting as was his craft German vocabulary, finding a term that means both Rift (split, break) and design (drawing). The drama of living derives from an irreducible opposition between Earth and World (nature and culture). Konsult is rift design (an assertion that must be developed elsewhere), taking up this enigmatic primordial experience of resistance encountered through living. Norbert Weiner, one of the inventors of cybernetics, defined life simply as anything that was negentropic, whether man or machine. We need to include in the drift of our posts a review of human capabilities, virtues, powers, the potentiality of egents which through education is realized in the service of well-being, thriving, living against disaster.
Capability. As these posts accumulate across an expanding set of categories, it is important to recall the focus of KE. Konsult learns the writing of the disaster in three dimensions: heuretics (invention), wide image (mystory), theopraxesis (capability). So far we have assumed some disaster addresses us, and devoted our attention to the heuretics of mystory, learning how to design an image of wide scope, source of our original hypothesis responding to disaster. Konsult takes up for electracy an ancient, even primordial drama: the striving to persist in one’s own being (to live), that Spinoza called Conatus, against the Overwhelming force of resistance, entropy, death. Heidegger characterized the drama as Riss, exploiting as was his craft German vocabulary, finding a term that means both Rift (split, break) and design (drawing). The drama of living derives from an irreducible opposition between Earth and World (nature and culture). Konsult is rift design (an assertion that must be developed elsewhere), taking up this enigmatic primordial experience of resistance encountered through living. Norbert Weiner, one of the inventors of cybernetics, defined life simply as anything that was negentropic, whether man or machine. We need to include in the drift of our posts a review of human capabilities, virtues, powers, the potentiality of egents which through education is realized in the service of well-being, thriving, living against disaster.
 The Way to Rainy Mountain. Son of a White mother and Kiowa father, Momaday was raised on a reservation. His novel House Made of Dawn won a Pulitzer Prize in 1969. His autobiographical The Way to Rainy Mountain was assigned as relay modeling the micro form and overall structuring by means of signifiers repeating across levels of the popcycle. Rainy Mountain juxtaposes Kiowa myths Momaday learned from his grandmother; the actual history of the Kiowa symbolized in the myths; his personal recollections of his childhood on the reservation. The text manifests identification (with his grandmother Aho and his grandfather Mammedaty); the use of pattern (the unity of each section is created by the repetition of a detail within the exposition across the three discourses); the use of setting to express feeling (the memories of scenes from the reservation). Most important is the location of Momaday’s memories of childhood in the context of the traditional stories and actual history of his Community (Kiowa), thus bringing the three levels of his symbolic experience into contact–personal, historical, mythical (entertainment fictions in a modern point of view). The book is a collection of thirty-four three-paragraph units (plus introduction and epilogue) illustrated with drawings by Momaday’s father. Unit 3 is cited as example: the popcycle sequence is always the same: Mythology; History; Memory.
The Way to Rainy Mountain. Son of a White mother and Kiowa father, Momaday was raised on a reservation. His novel House Made of Dawn won a Pulitzer Prize in 1969. His autobiographical The Way to Rainy Mountain was assigned as relay modeling the micro form and overall structuring by means of signifiers repeating across levels of the popcycle. Rainy Mountain juxtaposes Kiowa myths Momaday learned from his grandmother; the actual history of the Kiowa symbolized in the myths; his personal recollections of his childhood on the reservation. The text manifests identification (with his grandmother Aho and his grandfather Mammedaty); the use of pattern (the unity of each section is created by the repetition of a detail within the exposition across the three discourses); the use of setting to express feeling (the memories of scenes from the reservation). Most important is the location of Momaday’s memories of childhood in the context of the traditional stories and actual history of his Community (Kiowa), thus bringing the three levels of his symbolic experience into contact–personal, historical, mythical (entertainment fictions in a modern point of view). The book is a collection of thirty-four three-paragraph units (plus introduction and epilogue) illustrated with drawings by Momaday’s father. Unit 3 is cited as example: the popcycle sequence is always the same: Mythology; History; Memory. III
III