SINTHOME/Theopraxesis
Jacques Lacan, The Sinthome, Seminar XXIII, 1975-76
Lacan offered seminars annually from 1952 to 1980. Lacan’s seminars make an important contribution to the Theory in the CATTt guiding the invention of Konsult in general, and theopraxesis in particular. In this later seminar Lacan makes explicit some connections with the sources of our project that until now operated as assumptions. The first of these relationships is outlined here.
Capabilities.
Real, imaginary, and symbolic strikes me as just as valid as the other triad from which, going by Aristotle, the juice was extracted to compose man, namely, will, intelligence, and affectivity. (Sinthome 126).
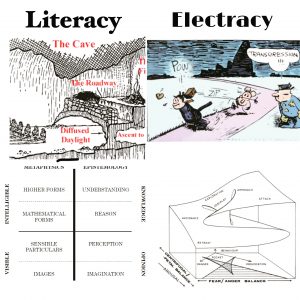
As discussed in the book, Konsult: Theopraxesis, one function of our experiment is to support a transition from literacy to electracy in education (to negotiate a passage from one apparatus to another). The pedagogy is centered on egents, the ones supposed to learn, appropriating the resources of Arts & Letters curriculum as means for students to undergo and develop their capabilities—their faculties, powers, virtues, potentiality—identified in the tradition dating from the invention of literacy in the Athenian academies as the embodied intellectual virtues: Theoria, Praxis, Poesis (theory, practice, poetics; thinking, doing, making; understanding, will, imagination). Kant’s Three Critiques take up this thread. The Third Critique promotes Aesthetics to equal status with Science and Morality, to propose aesthetic judgment as mediator bridging the abyss separating science and religion. Hannah Arendt took up Kant’s project as the best option for a Public Sphere in industrialized mass society after Auschwitz.
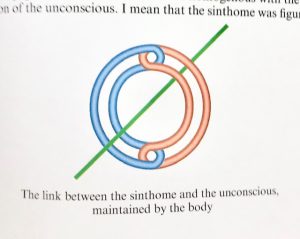
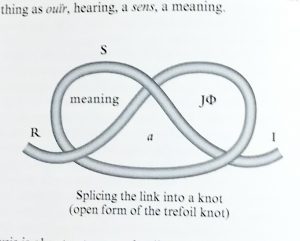
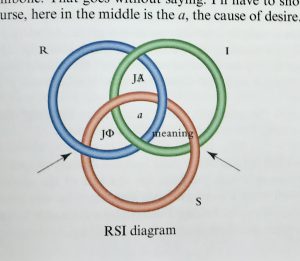
The importance of Lacan’s contribution is apparent in this context. His mnemonic image of the embodied virtues is a bag (the body, mathematically the empty set, the one) tied closed with cord (string, ficelles). RSI (playing on rhymes and puns with “heresy” and “airesis” or choice)—Lacan’s updating of the three faculties—Real, Symbolic, Imaginary—interrelate topologically, entangled in a way that Lacan explores through knot topology, with the Borromean knot specifically manifesting the sinthome (unique symptom). We have argued elsewhere that the sinthome helps account for the image of wide scope. One implication to be tested in our experiments is that in experience we encounter the apparatus stack (the popcycle) as entangled, knotted, in a manner articulated by topology. Lacan supplies one guide for the Kant-Arendt project, that we are calling theopraxesis: the virtues and their institutions already are fully integrated in a potential state (dunamis, but in a condition of privation, steresis). The “symptom” of this virtual condition is the polemos or seemingly irreducible conflict apparent in relations both macrocosmic and microcosmic of civilization.
HOGARTH: Line of Beauty
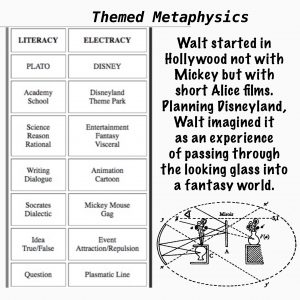
 A second affiliation with tradition important to note in this seminar is Lacan’s reference to Hogarth’s curved line of beauty as relevant to the genealogy of his knot topology. This connection makes explicit Lacan’s contribution to the larger question of the gramme, the invention of the plasmatic line in the Paleo apparatus, in continuing service up to the present, now augmented in electracy through animation and digital FX. Sergei Eisenstein cited Disney’s animated film, Steamboat Willie (1928) as a revelation of the new order opened up in media by the plasmatic line. We will have more to say about the ontological properties of this line.
A second affiliation with tradition important to note in this seminar is Lacan’s reference to Hogarth’s curved line of beauty as relevant to the genealogy of his knot topology. This connection makes explicit Lacan’s contribution to the larger question of the gramme, the invention of the plasmatic line in the Paleo apparatus, in continuing service up to the present, now augmented in electracy through animation and digital FX. Sergei Eisenstein cited Disney’s animated film, Steamboat Willie (1928) as a revelation of the new order opened up in media by the plasmatic line. We will have more to say about the ontological properties of this line.

MYSTORY: N. Scott Momaday
 The Way to Rainy Mountain. Son of a White mother and Kiowa father, Momaday was raised on a reservation. His novel House Made of Dawn won a Pulitzer Prize in 1969. His autobiographical The Way to Rainy Mountain was assigned as relay modeling the micro form and overall structuring by means of signifiers repeating across levels of the popcycle. Rainy Mountain juxtaposes Kiowa myths Momaday learned from his grandmother; the actual history of the Kiowa symbolized in the myths; his personal recollections of his childhood on the reservation. The text manifests identification (with his grandmother Aho and his grandfather Mammedaty); the use of pattern (the unity of each section is created by the repetition of a detail within the exposition across the three discourses); the use of setting to express feeling (the memories of scenes from the reservation). Most important is the location of Momaday’s memories of childhood in the context of the traditional stories and actual history of his Community (Kiowa), thus bringing the three levels of his symbolic experience into contact–personal, historical, mythical (entertainment fictions in a modern point of view). The book is a collection of thirty-four three-paragraph units (plus introduction and epilogue) illustrated with drawings by Momaday’s father. Unit 3 is cited as example: the popcycle sequence is always the same: Mythology; History; Memory.
The Way to Rainy Mountain. Son of a White mother and Kiowa father, Momaday was raised on a reservation. His novel House Made of Dawn won a Pulitzer Prize in 1969. His autobiographical The Way to Rainy Mountain was assigned as relay modeling the micro form and overall structuring by means of signifiers repeating across levels of the popcycle. Rainy Mountain juxtaposes Kiowa myths Momaday learned from his grandmother; the actual history of the Kiowa symbolized in the myths; his personal recollections of his childhood on the reservation. The text manifests identification (with his grandmother Aho and his grandfather Mammedaty); the use of pattern (the unity of each section is created by the repetition of a detail within the exposition across the three discourses); the use of setting to express feeling (the memories of scenes from the reservation). Most important is the location of Momaday’s memories of childhood in the context of the traditional stories and actual history of his Community (Kiowa), thus bringing the three levels of his symbolic experience into contact–personal, historical, mythical (entertainment fictions in a modern point of view). The book is a collection of thirty-four three-paragraph units (plus introduction and epilogue) illustrated with drawings by Momaday’s father. Unit 3 is cited as example: the popcycle sequence is always the same: Mythology; History; Memory.
III
Before there were horses the Kiowas had need of dogs. That was a long time ago when dogs could talk. There was a man who lived alone; he had been thrown away, and he made his camp here and there on the high ground. Now it was dangerous to be alone, for there were enemies all around. The man spent his arrows hunting food. He had one arrow left, and he shot a bear; but the bear was only wounded and it ran away The man wondered what to do. Then a dog came up to him and said that many enemies were coming; they were close by and all around. The man could think of no way to save himself. But the dog said: “You know, I have puppies. They are young and weak and they have nothing to eat. If you will take care of my puppies, I will show you how to get away.” The dog led the man here and there, around and around, and they came to safety.
A hundred years ago the Comanche Ten Bears remarked upon the great number of horses which the Kiowas owned. “When we first knew you, he said, “you had nothing but dogs and sleds.” It was so; the dog is primordial. Perhaps it was dreamed into being. The principal warrior society of the Kiowas was the Ka-itsenko, “Real Dogs,” and it was made up of ten men only, the en most brave. Each of these men wore a long ceremonial sash and carried a sacred arrow. In times of battle he must by means of this arrow impale the end of his sash to the earth and stand his ground to the death. Tradition has it that the founder of the Ka-itsenko had a dream in which he saw a band of warriors,, outfitted after the fashion of the society, being led by a dog. The dog sang the song of the Ka-itsenko, then said to the dreamer: “You are a dog; make the noise like a dog and sing a dog song.”
There were always dogs about my grandmother’s house. Some of them were nameless and lived a life of their own. They belonged there in a sense that the word “ownership” does not include. The old people paid them scarcely any attention, but they should have been sad, I think, to see them go.
Each numbered section is unified around one “pedagogical object”: arrow, spider, horse, hunting and the like. The importance of Mammedaty in this world is documented in unit XXI, in which Mammedaty appears in all three of the popcycle levels. The Disaster governing this world is that of the reservation itself, the destruction of the Kiowa people.
Assignment: Avatar Emergency 4
Kite@Ponte Vedra Beach. What is well-being? The Fifth Estate? The instruction is to document Event, Moment, of living, transferring from experience through photography to drawing.